In this digital era, where securing sensitive data is crucial, emerging technologies are reshaping how we verify users and control access to resources. Among these trends, biometric authentication and adaptive access control stand out, offering enhanced security and a smooth user experience. Let’s explore how these innovations are shaping the future of access management.
Biometric Authentication: Your Unique Digital Identity
No more worrying about remembering complicated passwords! Biometric authentication offers a user-friendly alternative using your distinct physical characteristics, like fingerprints, face, or voice, to grant access to your accounts and data. It’s like having a personalized key that only fits your digital locks!
Biometric authentication ensures that only you can access your accounts, providing a robust defense against unauthorized access.

Image Source: https://deeptechexpress.com/biometric-authentication-and-identification-systems-are-redefining-safety-standards/
Advantages of Biometric Authentication:
- Enhanced Security: Biometrics are unique physical traits, making it difficult for anyone else to access your accounts.
- Easy to Use: No need to remember passwords. Instead, you can use your fingerprint or face to log in.
- Lower Fraud Risk: Biometrics makes it hard for impostors to steal your identity or access your data.
- Not Easily Shared: Your biometric data is personal and can’t be easily shared or copied by others.
- Works for Many Users: Biometrics can accommodate many users, so it’s ideal for big organizations.
- Quick and Convenient: Biometric authentication is fast and convenient, saving you time and hassle.
Globally, 72% of customers prefer facial biometrics over passwords for safe online transactions.
Unimodal Vs. Multimodal Biometrics:
In a unimodal biometric security system, you only need one type of biometric, like a fingerprint, to get access. But in a multimodal biometric security system, you use two or more different biometrics, like both your fingerprint and face, as part of Multi-Factor Authentication.
According to Forbes, Justin Fulcher, Founder of RingMD, says there is a rising trend – a fusion of biometrics and behavioral analytics. This fusion can combine physical features like fingerprints and facial recognition with behavioral aspects like typing patterns to enhance security and make it harder for cybercriminals to mimic someone.
Adaptive Access Control (AAC): Smart Access for Your Digital World
Traditional access control methods can be rigid and inefficient, granting fixed permissions that may not always fit your needs. Enter Adaptive Access Control (AAC) – the intelligent system that dynamically adjusts access based on various factors.
It continuously monitors your behavior, location, and risk level in real-time. If it senses anything unusual, like someone trying to access your account from an unfamiliar device, it might ask for extra verification to ensure it’s you.
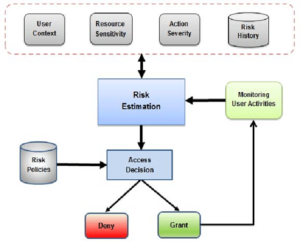
Image Source: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-proposed-adaptive-risk-based-access-control-model_fig2_317829147
Advantages of AAC:
- Enhanced Security: AAC adjusts access based on risk levels, reducing unauthorized entry. Trusted devices get more access than unknown ones.
- More Flexibility: It adapts access based on factors like time, location, and resource type, giving organizations better control.
- User-Friendly: It makes it easier for users by reducing authentication needs. Trusted devices can access resources without passwords, saving time.
Other Trends in IAM
Customer Identity and Access Management can use digital doubles to merge your identity and personality information, making your experience secure and personalized.
Zero trust is a cybersecurity trend that assumes nobody, not even devices, can be trusted. It keeps checking and allowing access for better security in modern work setups.
Single Sign-On (SSO) makes your online journey easy. It lets you access many things with just one click, saving time and making it safer by reducing password risks.


